Introduction to PVA Fiber: A Game-Changer in Cementitious Composites
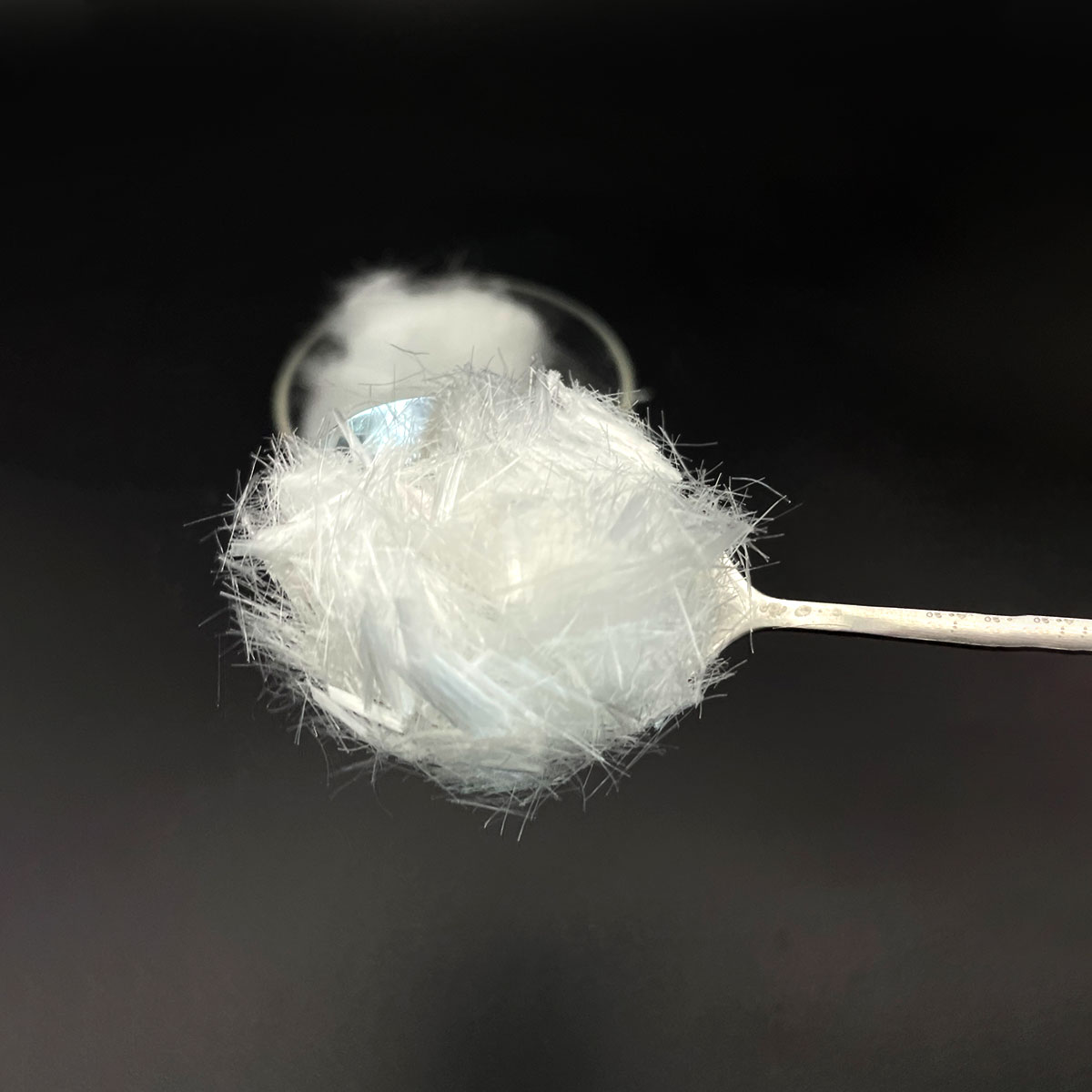
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) fiber has emerged as a leading strengthening material in modern cement-based compounds, reinventing the performance and toughness of concrete structures. Known for its high tensile strength, exceptional bond with cement matrices, and remarkable resistance to alkaline settings, PVA fiber is at the leading edge of advanced fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) modern technology. Its assimilation right into ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), crafted cementitious compounds (ECC), and strain-hardening cementitious materials (SHCM) notes a significant leap towards ductile, crack-resistant, and lasting building solutions.
(PVA Fiber)
Chemical and Mechanical Features of PVA Fiber
PVA fiber is an artificial polymer identified by high hydrophilicity, modest modulus of elasticity, and solid interfacial bonding with cementitious materials. Unlike steel fibers, which are vulnerable to corrosion, or polypropylene fibers, which offer limited mechanical reinforcement, PVA fibers incorporate flexibility with stamina– displaying tensile staminas going beyond 1,600 MPa and prolongation at break around 6– 8%. Their microstructure allows for reliable split connecting, power dissipation, and post-cracking ductility, making them excellent for applications calling for toughness and effect resistance without endangering workability.
Mechanism of Fracture Control and Ductility Improvement
The primary function of PVA fiber in concrete is to control microcrack breeding and enhance post-cracking actions. When consistently dispersed within the matrix, PVA fibers act as micro-reinforcement elements that bridge cracks started during packing or shrinkage. This mechanism considerably boosts flexural stamina, fracture sturdiness, and power absorption capability. In Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC), PVA fibers enable strain-hardening habits, where the product displays multiple fine splits instead of tragic failing. This one-of-a-kind building simulates the ductility seen in steels, changing generally weak concrete right into a quasi-ductile product ideal for seismic-resistant and fatigue-prone frameworks.
Applications in Infrastructure, Fixing, and Prefabricated Systems
PVA fiber-reinforced concrete is increasingly made use of in facilities tasks requiring high sturdiness and strength. It plays a crucial duty in tunnel cellular linings, bridge decks, water containment frameworks, and blast-resistant buildings as a result of its capacity to withstand spalling under extreme problems. In architectural repair and retrofitting, PVA-modified mortars supply enhanced attachment, lowered shrinking cracking, and enhanced long-lasting efficiency. Upreared parts including PVA fibers take advantage of controlled breaking, dimensional stability, and much faster demolding cycles. In addition, its compatibility with automated casting procedures makes it appropriate for modular and 3D-printed construction systems.
Sustainability and Environmental Perks
Past mechanical efficiency, PVA fiber adds to sustainable building and construction practices. By allowing thinner, lighter, and longer-lasting structures, it decreases total material intake and embodied carbon. Compared to steel fiber-reinforced concrete, PVA fiber removes issues related to corrosion discoloration and galvanic deterioration, extending service life and decreasing upkeep expenses. Some formulations now integrate bio-based or partly biodegradable variants, aligning with environment-friendly structure requirements and circular economic climate principles. As environmental laws tighten up, PVA fiber presents a feasible alternative that stabilizes architectural honesty with eco-friendly responsibility.
Obstacles and Limitations in Practical Application
In spite of its advantages, the adoption of PVA fiber faces challenges connected to cost, diffusion, and healing level of sensitivity. PVA fibers are more pricey than standard artificial fibers, limiting their usage in budget-sensitive applications. Achieving consistent diffusion needs specialized mixing methods, as improper handling can result in balling or segregation. Additionally, PVA fibers are delicate to long term wet-dry cycling, which may influence long-term bond performance otherwise sufficiently dealt with fiber surface treatment or hybrid fiber approaches. Addressing these issues calls for ongoing research right into economical production techniques and performance optimization.
Technologies Driving Next-Generation PVA Fiber Technologies
( PVA Fiber)
Continuous advancements in fiber design are broadening the capacities of PVA fiber in building and construction. Surface adjustment techniques such as plasma therapy, etching, and finish with nano-silica or polymer layers are enhancing fiber-matrix interaction and longevity. Hybrid systems integrating PVA with other fibers– such as carbon or basalt– are being checked out to enhance mechanical homes throughout various packing circumstances. Scientists are also creating clever PVA fibers installed with sensing capabilities for real-time architectural health monitoring. These developments are pushing the boundaries of what fiber-reinforced concrete can accomplish, leading the way for smart, adaptive structure products.
Market Fads and International Market Overview
The worldwide market for PVA fiber in building is expanding steadily, driven by increasing demand for high-performance concrete in Asia-Pacific, The United States And Canada, and Europe. Governments and sector leaders are investing in resilient facilities, catastrophe reduction, and sustainable urban growth– key vehicle drivers for PVA fiber fostering. Leading chemical and construction material suppliers are increasing product, boosting technical support, and working together with academic institutions to fine-tune application procedures. Digital devices such as AI-driven mix style software application and IoT-enabled fiber dosing systems are additional streamlining execution, enhancing effectiveness, and guaranteeing constant high quality across large projects.
Future Potential Customers: Integration with Smart and Resilient Building And Construction Ecosystems
Looking ahead, PVA fiber will play a central role in shaping the future generation of clever and resistant construction ecological communities. Assimilation with electronic twin platforms will enable engineers to imitate fiber-reinforced concrete habits under real-world conditions, optimizing design before implementation. Developments in self-healing concrete including PVA fibers and microcapsules are anticipated to expand structural life-spans and decrease lifecycle expenses. Moreover, as the construction industry accepts decarbonization and automation, PVA fiber sticks out as a vital enabler of lightweight, high-strength, and environmentally receptive building materials tailored for the future.
Supplier
Cabr-Concrete is a supplier of Concrete Admixture under TRUNNANO with over 12 years of experience in nano-building energy conservation and nanotechnology development. It accepts payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union and Paypal. TRUNNANO will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by air, or by sea. If you are looking for high quality what is pva fiber, please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry(sales5@nanotrun.com).
Tags: pva fiber,polyvinyl alcohol fiber, pva concrete
All articles and pictures are from the Internet. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us in time to delete.
Inquiry us